What Is Cyber Security?

Cyber Security Definition
Cyber security has become a buzzword lately. It can often come across as a tactic used by insurance companies and agents to instill a sense of paranoia, in hopes that you purchase a policy. We here at EINSURANCE aim to demystify this notion of cyber security and arm you with facts, so that you are better equipped to decide:
- if you have exposure
- if you do, what coverages, specifically, are needed.
Formally, cyber security is defined as, “measures taken to protect against criminal or unauthorized use of electronic data.” Similar to the definition of “security,” just in this case we’re referring to digital assets/property, not physical ones. The definition alone shows the general and expansive nature of cyber security. Unfortunately, it’s not confined to one industry, but creates exposure to everyone operating in the current economy. This risk expands as the digital market increases in size.
First, we’ll take a look at the actual rise in awareness and exposure of cyber security, then we’ll place a magnifying glass on specific exposures that could be impacting your business, and review ways to mitigate that exposure.
Increase in Cyber Crime
The graph below provides an idea of the cyber crime trend. Although the amount of records stolen has generally averaged circa 90 million records/year between 2005-2017, there is a strong positive slope regarding the amount of data breaches that have occurred in that same period of time. The central driver to this trend is the fact that we are becoming a far more digital economy every day.
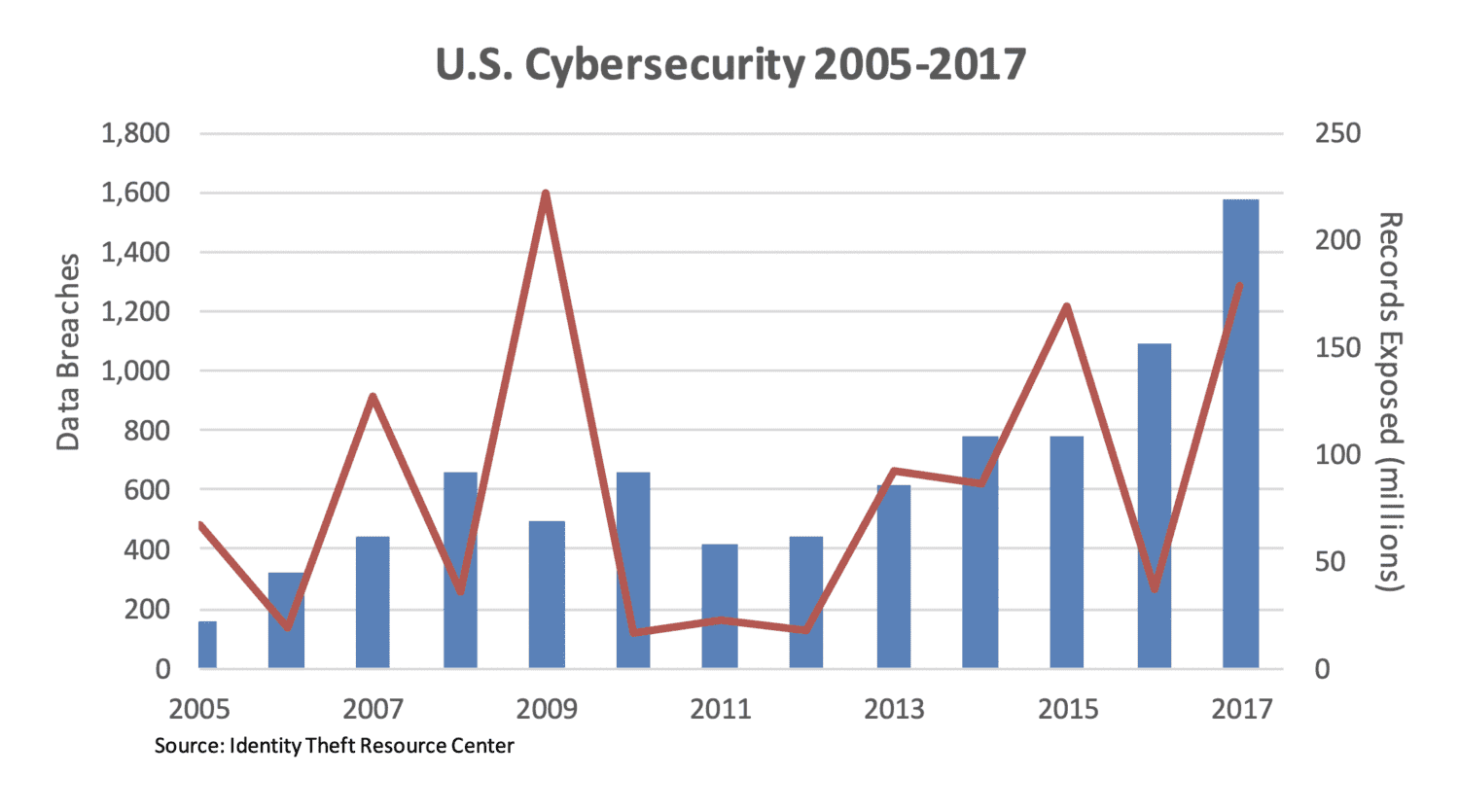
Two decades ago, people just weren’t as comfortable transacting, researching, or simply operating online, as they are today. This explosion of the digital market provides bad actors ample opportunities to attempt to steal your personal information for their financial gain. Below are a few of the most well-known breaches that have occurred over the past few decades.
- Yahoo!: 3 billion records – December 2016 Yahoo reported hackers stole names, email addresses, birth dates, passwords and other personal information during a breach in 2013.
- Yahoo!: 500 million records – September 2016 Yahoo reported hackers stole names, email addresses, birth dates, passwords and other personal information during a breach in 2014.
- Under Armour: 150 million records – March 2018 Under Armour reported that a breach affected customers that used its food and nutrition application, MyFitnessPal, and usernames, email addresses and passwords were compromised.
- Ebay: 145 million records – May 2014 Ebay reported that their consumer database of usernames, passwords, physical addresses and phone numbers had been hacked.
- Equifax: 143 million records – September 2017 Equifax reported that consumers social security numbers, birthdates, drivers’ licenses and other data were stolen from their site.
- TJ Maxx: 94 million records – October 2007, TJX Cos. Reported that its customer Visa and Mastercard accounts were exposed in a fraud data breach.
- AOL: 92 million records – June 2004 AOL reported that an engineer stole the company’s customer lists and sold it to an online marketer.
- Anthem Inc.: 80 million records – February 2015 Anthem, Inc. disclosed that personal identifiable information of their patients was stolen from their servers.
- Sony Playstation: 77 million records – April 2011 Sony Playstation reported the theft of names, addresses and credit card information from its customer’s accounts.
- JP Morgan Chase: 76 million records – October 2014 JPMorgan Chase & Co. announced information regarding customers had been compromised.
Source: Wikipedia
How to Respond to a Cyber Attack
The underlying theme conveyed by this random list of the U.S.’ most well know breaches isn’t the breadth of people affected, but the diversity of the industries represented. Whether its retail, financial services, or healthcare, all facets of our economy are susceptible to the intrusive nature of cybercrime. Each of these companies endured a similar process when their customer’s information was compromised. This process can shed light on exposure that you, and the overall economy face. Let’s take a closer look at each phase:
Phase I: Freeze Everything: After recognizing your customers’ (or employees’) information have been compromised, its best to go into hibernation mode, as continuing to operate in the current state could lead to more confidential information leaking.
Phase II: Audit Systems: After recognizing the hack, or theft of information, you now must complete a thorough assessment of what happened and ascertain what systems, and more importantly, who has been affected.
Phase III: Initiate Plan to Fortify Systems: Now that you have the diagnosis and understanding of the damage, it’s now time to address the problem through implementing cyber security measures that prevent such an attack in the future. This stage may become standard operating procedure, as cyber criminals continue to find creative ways to thwart cyber security systems.
Phase IV: Notify Customers/Public: Perhaps the most painful part of this process, now its time to notify your customers of what has transpired, who’s information has been compromised, and what has been done, including what will be done in the future, to prevent this from happening again.
What Cyber Insurance Should You Get to Protect Your Small Business Against Cyber Attack
Although a condensed version of the multiple steps taken when your customers’ personal information has been compromised, it provides a good snapshot of the process of recovery. As you can see, operations can be halted, or at the very least, slowed down for a great deal of time depending on how long it takes you to get through the first three phases. This slow down in operations, tends to have a negative impact on revenue, which is an important coverage benefit of a cyber security policy. Calculating loss of revenue due to your systems being down tends to be more art than science, so when reviewing a cyber security policy, make sure you have adequate limits here.
Another large exposure created by such a breach is the direct expenses associated with recovery:
- Hiring a 3rdparty to assess the damage and implement measures to prevent future breaches (Phase III)
- Any legal costs, or mitigants to legal costs (providing credit monitoring and/or counseling services for your customers) associated with Phase IV
Both can be covered within policy limits within your cyber security policy. Another exposure that could cause your firm heartache, but you may find it hard to get your carrier to cover it, is damage to your brand. Due to the difficulty to quantify the revenue impact of loss of brand strength, most carriers will be hesitant to provide such coverage, however, you should certainly inquire about it.
Cyber insurance coverage is relatively new to the insurance industry. Thus, carriers and customers alike are navigating through it carefully. As a result, pricing and coverage is often customized and differs dramatically from carrier to carrier. As such, make sure you use the above analysis as a guideline to review your business, any exposure you may have and to craft cyber security coverage that is unique to your business model and covers you properly. As you do so, let EINSURANCE help you find that carrier that can best partner with you to achieve your cyber insurance coverage goals.

 EINSURANCE
EINSURANCE EINSURANCE
EINSURANCE EINSURANCE
EINSURANCE